| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 후기
- 태블로
- 태블로 무료 강의
- CourseraSQL
- 빅데이터분석기사
- tableau
- 태블로 데스크탑
- 태블로 신병훈련소
- 태블로 자격시험 독학
- Python
- python udemy
- 태블로 신병훈련소 후기
- 태블로 리뷰
- 태블로초보
- SQL
- TABLEAU Certificate
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 10기
- 알약 모양
- 태블로독학
- 태블로 자격증 독학
- 태블로 신병 훈련소
- 범프차트
- coursera
- 태블로 자격시험
- 데이터 시각화
- 태블로 씹어먹기
- 태블로 독학
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 11기
- 태블로신병훈련소
- 태블로 집합
- Today
- Total
하루에 하나씩
Python basic - .format & List & Tuples & Dictionaries 본문
Python prefers snake casing
- if you have multiple words inside a variable name, you separate them out by underscores.
ex. name_of_var = 2
print() function
no quotes, no out cell

.format()
insert objects into a string.


Label the variables
The point is that we don't need to worry about the order


List (=arrays in other languages)

Using indexing
- Python supports negative indexing
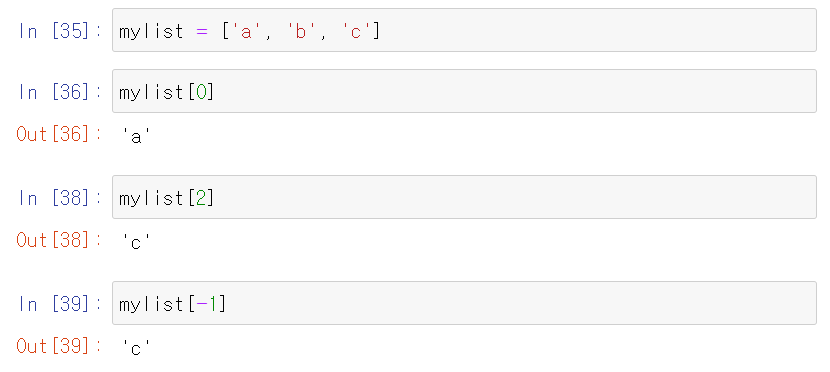
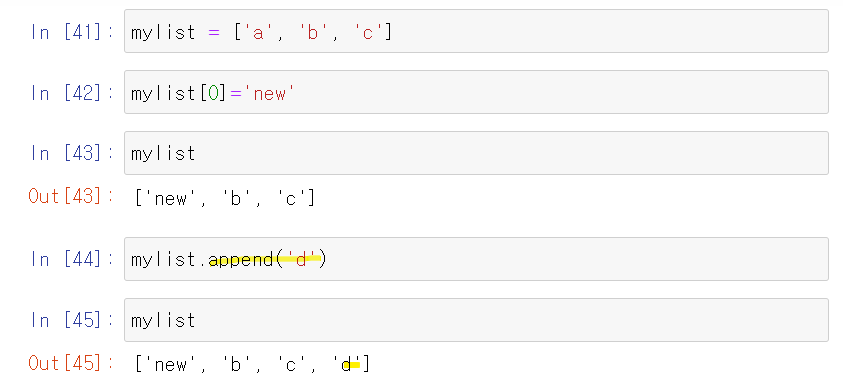
Changing an item in the list
- 변경 후 run하면 변경사항이 안보이지만, 리스트를 다시 run하면 변경사항이 나타난다.

Appending item in the list
list.append('')
Grabbing an item in the nested list

Dictionaries aka hash tables in other languages
* dictionaries in python do not retain any order
This is a really great way to store things where you need really quick access.

Boolean
False = 0
True = 1
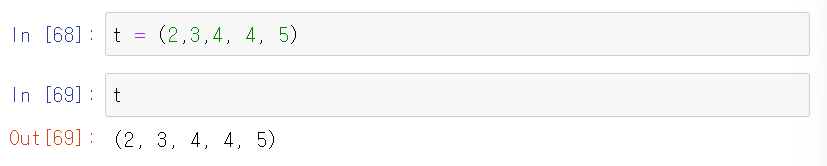
Tuples
- parenthesis 사용
- Tuples are immutable(can't reassign the items
Compare to the list, in Tuples, a user can't change anything inside of this sequence

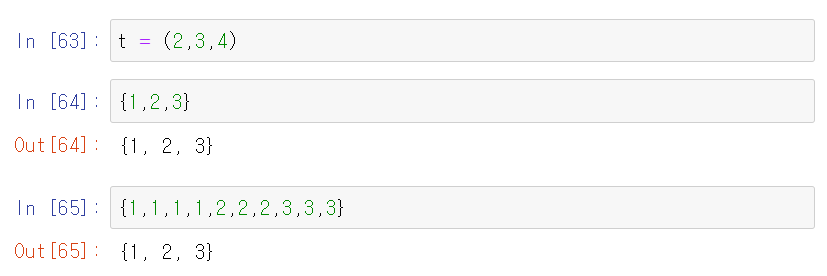
Sets
- Looks a lot like a dictionary, except there's no key value pair.
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python Basic - 02-Python Crash Course Exercises (0) | 2023.10.01 |
|---|---|
| Python basic - Function & Method (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| Python Basic - Comparison operator & Logic operator (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| [Python] 2. Expressions (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| [Python] 1. Python3, Editor 설치와 터미널 사용하기 (0) | 2023.01.03 |




