| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- 태블로 신병훈련소
- 알약 모양
- 태블로 신병훈련소 후기
- 태블로 독학
- Python
- 태블로 리뷰
- 태블로독학
- 태블로 자격시험
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 11기
- coursera
- 태블로 신병 훈련소
- TABLEAU Certificate
- 태블로신병훈련소
- 태블로초보
- 태블로 씹어먹기
- 태블로 자격시험 독학
- 빅데이터분석기사
- 태블로 데스크탑
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 10기
- CourseraSQL
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 후기
- 태블로
- tableau
- 태블로 집합
- 데이터 시각화
- 태블로 자격증 독학
- SQL
- 태블로 무료 강의
- python udemy
- 범프차트
- Today
- Total
하루에 하나씩
Section 4: NumPy - NumPy Arrays 본문
13. Introduction of NumPy
Section Goal
- Understand Numpy
- Create arrays with Numpy
- Retrieve information from a NumPy array through slicing and indexing
- Learn basic NumPy operations
- Test NumPy skills with exercise questions.
What is NumPy?
- Python library for creating N-dimensional arrays
- Ability to quickly broadcast functions
- Built-in linear algebra, statistical distributions, trigonometric, and random number capabilities
Why use NumPy?
- While NumPy structures look similar to standard Python lists, they are much more efficient
- The broadcasting capabilities are also extremely useful for quickly applying functions to our data sets
NumPy Arrays
Numpy를 library로 import하기

# NumPy Arrays
NumPy arrays are the main way we will use NumPy throughout the course. NumPy arrays essentially come in two flavors: vectors and matrices. Vectors are strictly 1-dimensional (1D) arrays and matrices are 2D (but you should note a matrix can still have only one row or one column).
# Why use Numpy array? Why not just a list?
There are lot's of reasons to use a Numpy array instead of a "standard" python list object. Our main reasons are:
* Memory Efficiency of Numpy Array vs list
* Easily expands to N-dimensional objects
* Speed of calculations of numpy array
* Broadcasting operations and functions with numpy
* All the data science and machine learning libraries we use are built with Numpy

# Creating NumPy arrays from Objects
From a Python List
We can create an array by directly converting a list or list of lists :
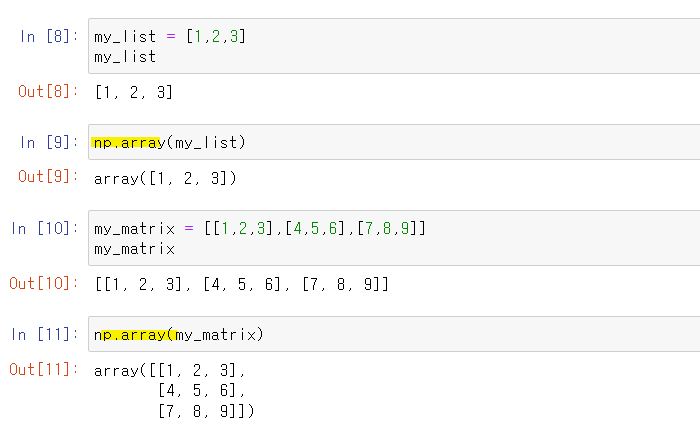
# Built-in Methods to create arrays
There are lots of built-in ways to generate arrays.
arange
Return evenly spaced values within a given interval [reference]

zeros and ones
Generate arrays of zeros or ones. [reference]

linspace
Return evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval. [reference]
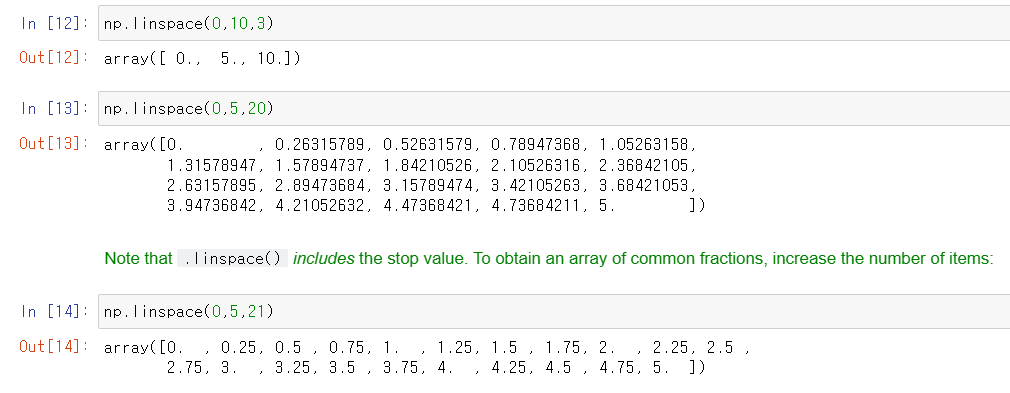
eye
Creates an identity matrix [reference]

# Random
Numpy also has lots of ways to create random number arrayas:
rand
Creates an array of the given shaped and populates it with random samples from a uniform distribution over [0,1) [reference]

randn
Returns a sample(or samples) from the "standard normal" distribution [σ = 1]. Unlike rand which is uniform, values closer to zero are more likely to appear. [reference]
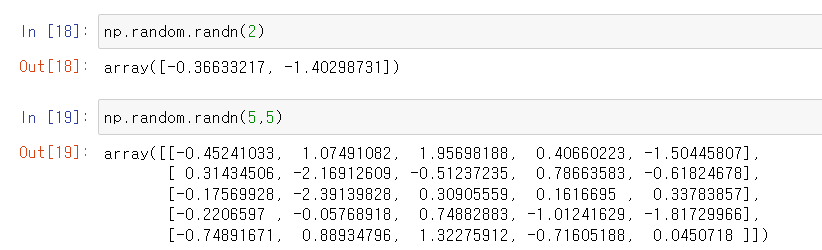
randint
Returns random integers from low(inclusive) to high(exclusive). [reference]

seed
can be used to set the random state, so that the same "random" results can be reproduced [reference]

# Arrays
Let's discuss some useful attributes and methods for an array:

Reshape
Returns an array containing the same data with a new shape. [reference]
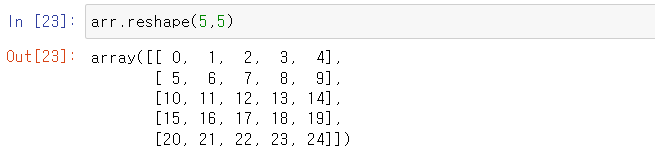
max, min, argmax, argmin
These are useful methods for finding max or min values. Or to find their index locations using argmin or argmax

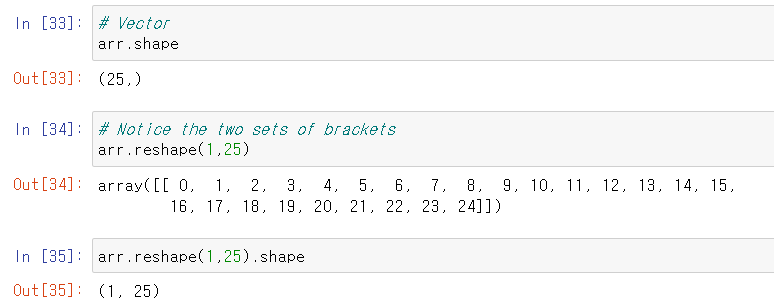
Shape
Shape is an attribute that arrays have (not a method): [reference]

dtype
You can also grab the data type of the object in the array: [reference]

'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Section 3: Machine Learning Pathway Overview (0) | 2023.10.03 |
|---|---|
| Python Basic - 02-Python Crash Course Exercises (0) | 2023.10.01 |
| Python basic - Function & Method (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| Python Basic - Comparison operator & Logic operator (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| Python basic - .format & List & Tuples & Dictionaries (0) | 2023.08.13 |




