[SQL] (1Week) Selecting and Retrieving Data with SQL
Data Models
Database: A container(usually a file or set of files) to store organized data; a set of related information
Table: A structured list of data or a specific type
Column: A single field in a table - all tables are made up of one or more columns.
Row: A record in a table
Data modeling
- Organizes and structures information into multiple related tables
- Can represent a business process or show relationships between business processes
- Should closely represent real world
Types of Data Models
- Models for prediction built by data scientists
- Data model as data tables represented and organized in a database
Evolution of Data Models

* NoSQL came onto the scene around 2009
SQL in a Big Data World
NoSQL - Not Only SQL
A mechanism for storage and retrieval of unstructured data modeled by means other than tabular relations in relational databases.
Relational vs Transactional Model
Relational Model: Allows for easy querying and data manipulation in an easy, logical, and intuitive way.
Transactional Model: Operational database- insurance claims within a healthcare database
Data Model Building Blocks
Entity: Person, place thing, or event. Distinguishable, unique, and distinct
Attribute: A characteristic of an entity
Relationship: Describes association among entities
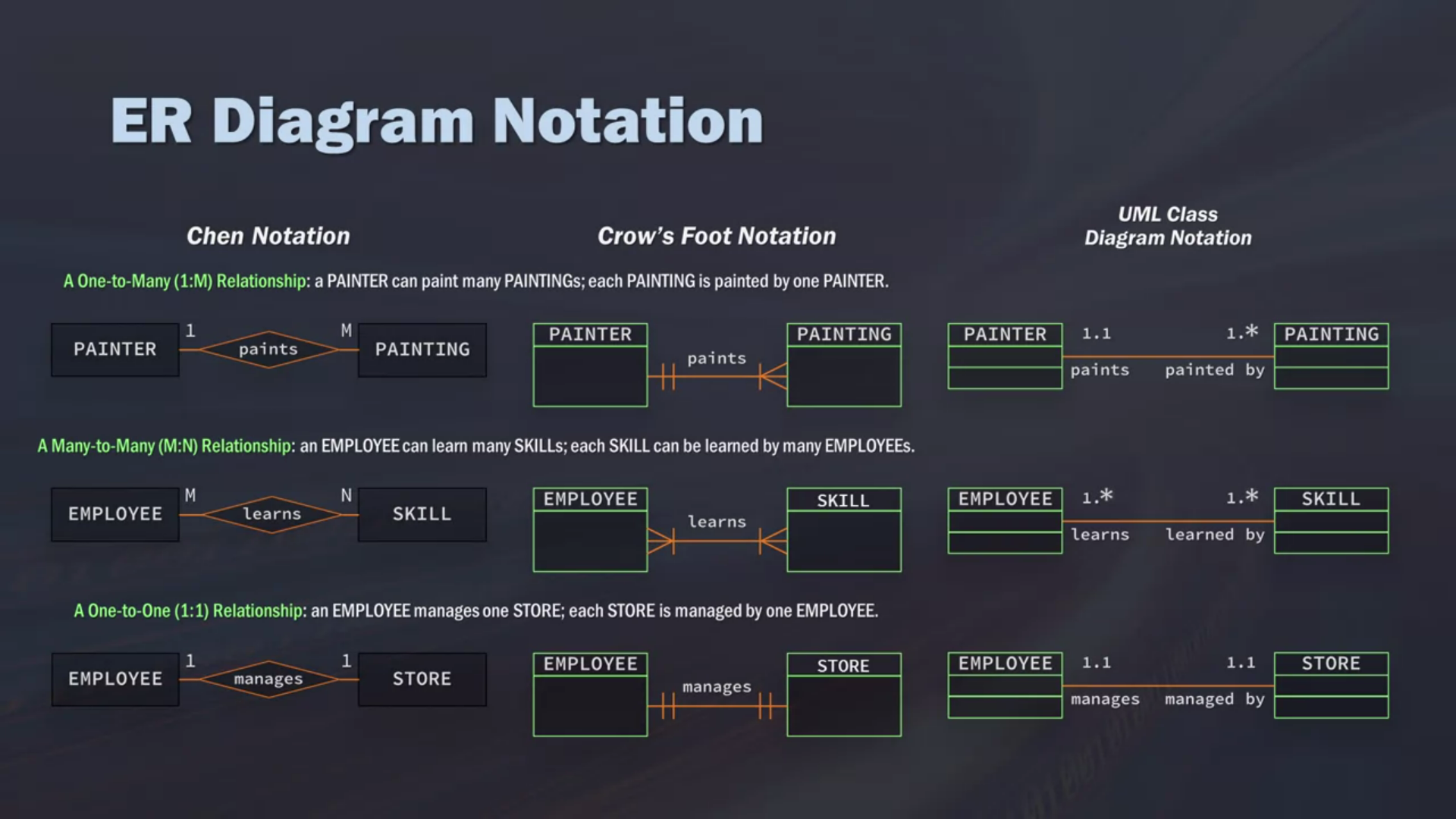
- One-to-many: customer to invoices
- Many-to-many: student to classes
- One-to-one: manager to store
ER Diagrams
ER model is composed of entity types and specifies relationships that can exist between instances of those entity types
- Show relationships
- Business process
- Represented visually
- Show links(primary keys)
Primary key vs Foreign key
Primary key
: a column(or set of columns) whose values uniquely identify every row in a table
Foreign key
: One or more columns that can be used together to identify a single row in another table
ER Diagram Notation
Chen notation/ Crow's Foot Notation/ UML Class Diagram Notation
Retrieving Data with a SELECT Statement
The SELECT Statement
Need to specify two pieces of information to use a SELECT statement: what you want and where you want to select it from

Retrieving Multiple Columns
Add multiple column names, be sure to use a comma

Retrieving Multiple Columns Using a Wild card
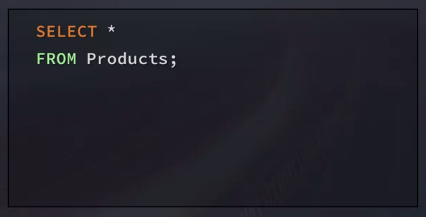
Request all columns by using the asterisk(*) wildcard character instead of column names
Why Limit Results?
If your database is large. You might only want to see a sample of the data


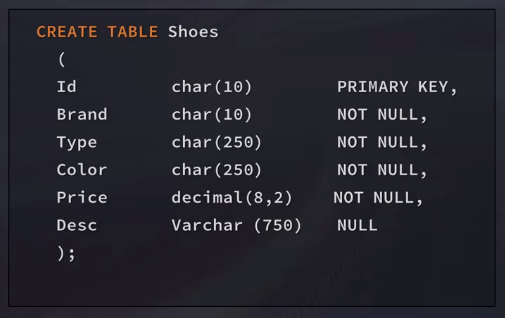
Creating Tables
Creating tables
Nulls and Primary Keys
- Every column is either NULL or NOT NULL
- An error will be returned if one tries to submit a column with no value
- Don't confuse null values with empty strings
- Primary keys can not be null
- Primary Keys MUST have a value
Adding Data to the Table
INSERT INTO

Creating Temporary Tables
Why create temporary tables?
Temporary tables will be deleted when the current session is terminated
Faster than creating a real table
Useful for complex queries using subsets and joins
How to Create a Temporary Table


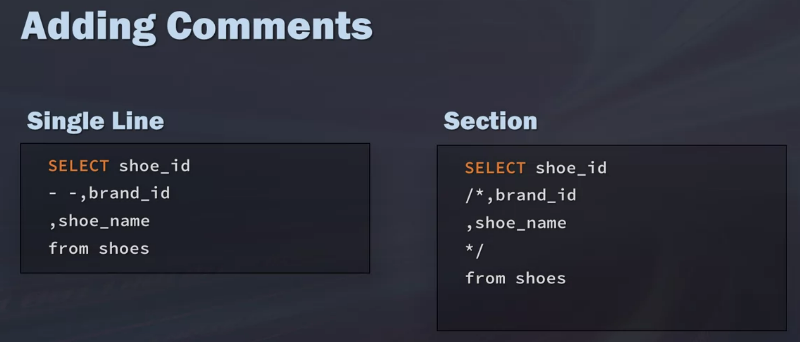
Adding Comments to SQL
Why Add comments
Help you remember what you were doing and why
Mute the expression of code(commenting out code)
Troubleshoot query issues systematically
Source Code Editors
Environment separate from the database where you can write and edit code
e.g. Notepad++
SQL Overview
This module's primary focus was to introduce the world of SQL to you and to get you started with a few simple querying techniques. Attached to this posting, are a few good, quality overviews of SQL that go into a little bit more depth than what we can cover in our lecture videos. I encourage you to check out and review one or more of these resources.
Data Modeling and ER Diagrams
We introduced ER diagrams and the concept of database modeling in this module. Naturally, these are deep topics and we barely scratched the surface in our lecture videos. I encourage you to review some of the resources below to learn more about these topics in more depth.