| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- CourseraSQL
- 데이터 시각화
- 태블로초보
- tableau
- 태블로 신병 훈련소
- SQL
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 10기
- Python
- 알약 모양
- 태블로신병훈련소
- 태블로 데스크탑
- 태블로 신병훈련소 후기
- 태블로 리뷰
- python udemy
- TABLEAU Certificate
- 태블로 씹어먹기
- 태블로 독학
- coursera
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 후기
- 태블로 집합
- 태블로 신병훈련소
- 태블로 신병 훈련소 11기
- 범프차트
- 태블로독학
- 태블로 자격시험
- 태블로 자격시험 독학
- 태블로
- 태블로 무료 강의
- 태블로 자격증 독학
- 빅데이터분석기사
- Today
- Total
하루에 하나씩
[SQL] (3Week) Subqueries and Joins in SQL 본문
<목차>
Subqueries and Joins in SQL
- Module Introduction
- Using Subqueries
- Subquery Best Practices and Considerations
- Joining Tables: An Introduction
- Cartesian (Cross) Joins
- Inner Joins
- Aliases and Self Joins
- Advanced Joins: Left, Right, and Full Outer Joins
- Unions
- Practice Quiz - Writing Queries
- Summary
- 읽기 자료: SQL and Python
- 읽기 자료: Union and Union All
1. Module Introduction
Subqueries
- How they work
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Best practices for using subqueries
Joins
- Revisit key fields
- Linking data together with joins
- Characteristics of different types of joins
Making Code Cleaner and Efficient
- Using alias and pre-qualifiers
2. Using subqueries
What are Subqueries?
- Queries embedded into other queries
- Relational databases store data in multiple tables
- Subqueries merge data from multiple sources together
- Helps with adding other filtering criteria
Data scientists often use subqueries to select specific records or columns and then use that criteria as a filtering criteria for the next thing they want to select. Not only are subqueries helpful when it comes to getting information from multiple tables, but they're often used for adding additional criteria like filtering criteria that's not in your current table from another table into your query.
Problem Set up: Subqueries to Filter
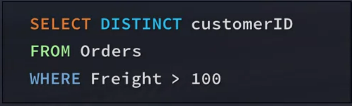
Need to know the region each customer is from who has had an order with freight over 100
1. Retrieve all customer IDs for orders tih freight over 100
2. Combilne the two queries
Example
Need to know the region each customer is from who has had an order with freight over 100

Combined for a Subquery
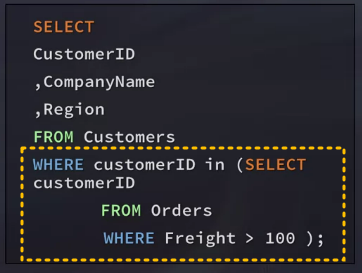
Working with Subquery Statements
Always perform the innermost SELECT portion first

DBMS is performing two operations
1. Getting the order numbers for the product selected
2. Adding that to the WHERE clause and processing the overall SELECT statement
3. Subquery Best Practices and Considerations
Learning Objectives
- Discuss how to write subqueries within subqueries
- Discuss performance limitations with overuse of subqueries
- Explain how to use subqueries as calculations
- Describe best practices using subqueries
Best Practices with Subqueries
- There is no limit to the number of subqueries you can have
- Performance slows when you nest too deeply
- Subquery selects can only retrieve a single column
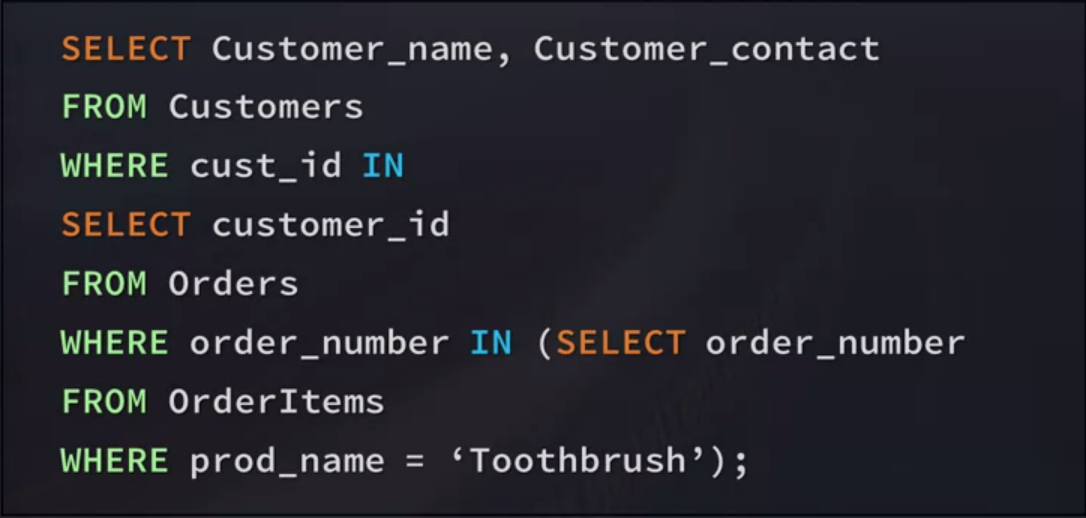
Subquery in Subquery
1. Order numbers for toothbrushes
2. Customer ID's for those orders
3. Customer information for those orders
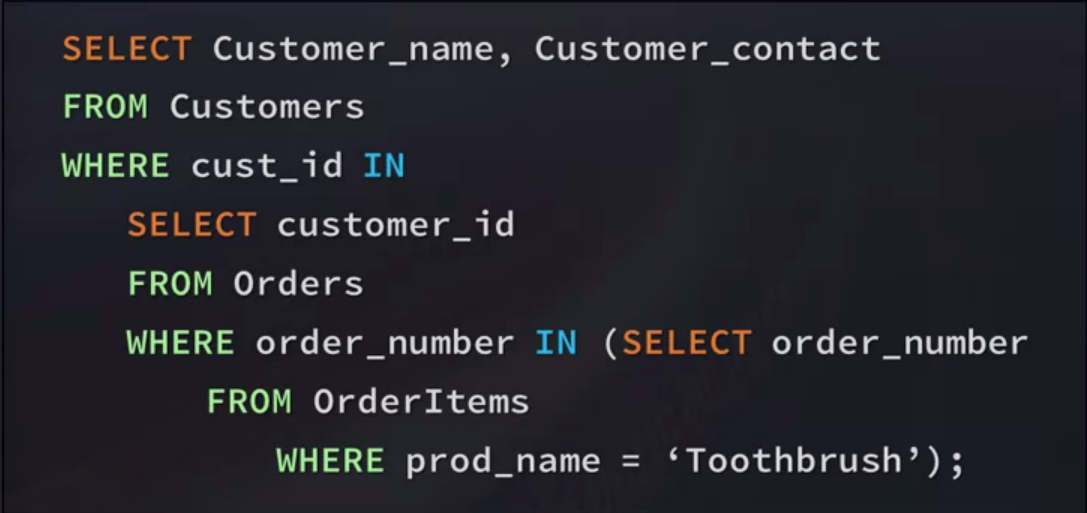
PoorSQL Website
Poor SQL - Instant Free and Open-Source T-SQL Formatting
poorsql.com
- The website will pre-format code
- Uses proper indenting
- Code is easier to read and troubleshoot
Subqueries for Calculations
Total number of orders placed by every customer


4. Joining Tables: An Introduction
Learning Objectives
- Discuss the benefits of a relational database system
- Describe what a JOIN is and how to use the JOIN function to combine information from multiple tables
- Describe how a key field is used to link data together
Benefits of Breaking Data into Tables
- Efficient storage
- Easier manipulation
- Greater scalability
- Logically models a process
- Tables are related through common values (keys)
Joins
- Associate correct records from each table on the fly
- Allows data retrieval from multiple tables in one query
- Joins are not physical - they persist for the duration of the query execution
5. Cartesian (Cross) Joins
Learning Objectives
- Define Cartesian(or Cross) joins
- Describe some specific cases where Cartesian joins are useful
- Write the appropriate SQL syntax to establish a Cartesian join
What is a Cartesian (Cross) Join?
Cross JOINs: each row from the first table joins with all the rows of another table
If you have a table with just 10 records in it and the second table with 10 records, just performing a cross join is already going to increase it to 100. And rarely are you ever working with a table with just ten records.
Cartesian(Cross) Join Example

└Times every record in the first table by the number in the second table, we don't need any key or qulification.

Output will be the number of joins in the 1st table multiplied by the number of rows in the 2nd table.
Cartesian (Cross) Joins
- Not frequently used
- Computationally taxing
- Will return products with the incorrect vendor or no vendor at all
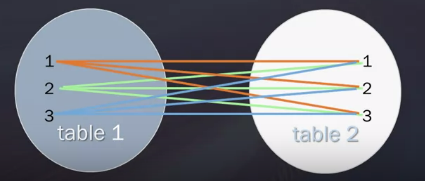
6. Inner Join
Learning Objectives
- Define and describe an inner join
- Explain when and how to use an inner join
- Pre-qualify column names to make your SQL code that much cleaner and efficient
What is an Inner Join
The INNER JOIN keyword selects records that have matching values in both tables
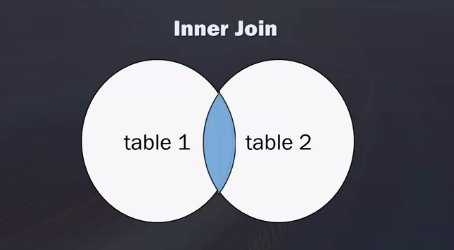
Inner Join Example
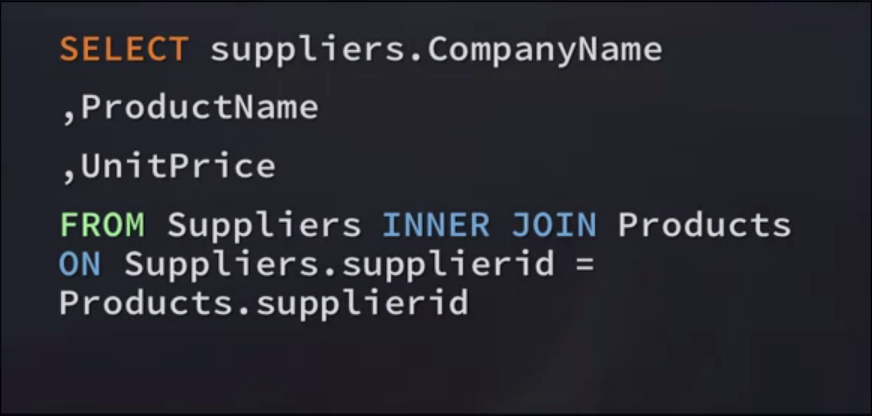
Inner Join Syntax
- Join type is specified(INNER JOIN)
- Join condition is the FROM clause and uses the ON clause
- Joining more tables together affects overall database performance
- You can join multiple tables, with no limit
- List all the tables, then define conditions
Inner Join with Multiple Tables

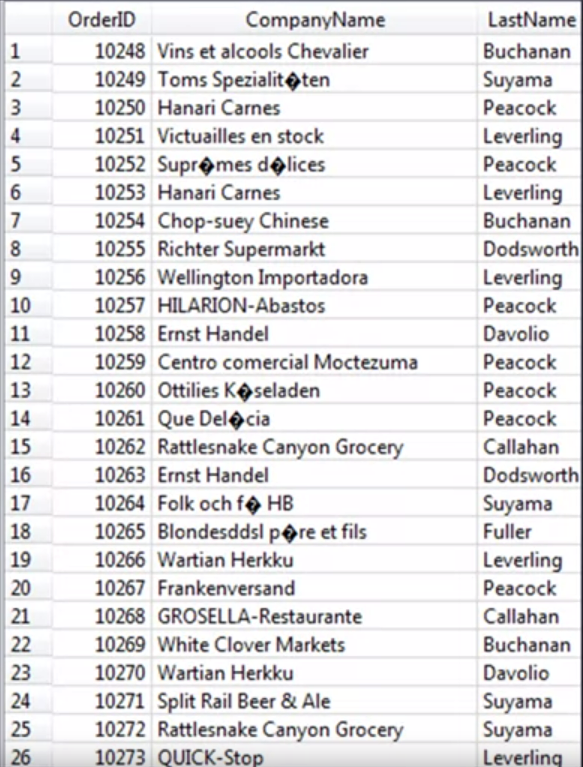
Best Practices With Joins
- Make sure you are pre-qualifying names
- Do not make unnecessary joins
- Think about the type of join you are making
- How are you connecting records
7. Aliases and Self Joins
What Is an Alias
- SQL aliases give a table or a column a temporary name
- Make column names more readable
- An alias only exists for the duration of the query
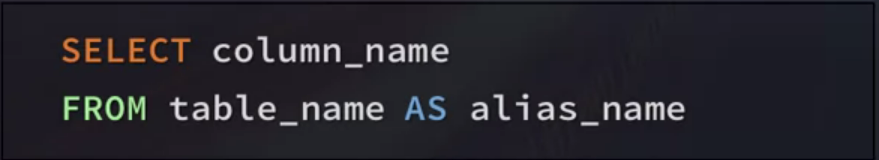
Query Example Using Alias

Self Joins
- Match customers from the same city
- Take the table and treat it like two separate tables
- Join the original table to itself

Self Join Example
The following SQL statement matches customers that are from the same city:

8. Advanced Joins: Left, Right, and Full Outer Joins
SQL Lite vs other SQL DBMS
- SQL Lite only does Left Joins
- Other database management systems use all joins
Learning Objectives
- Explain how left, tight, and full outer joins work
- Identify situations to use each type of join
- Use each type of join to combine data from multiple tables
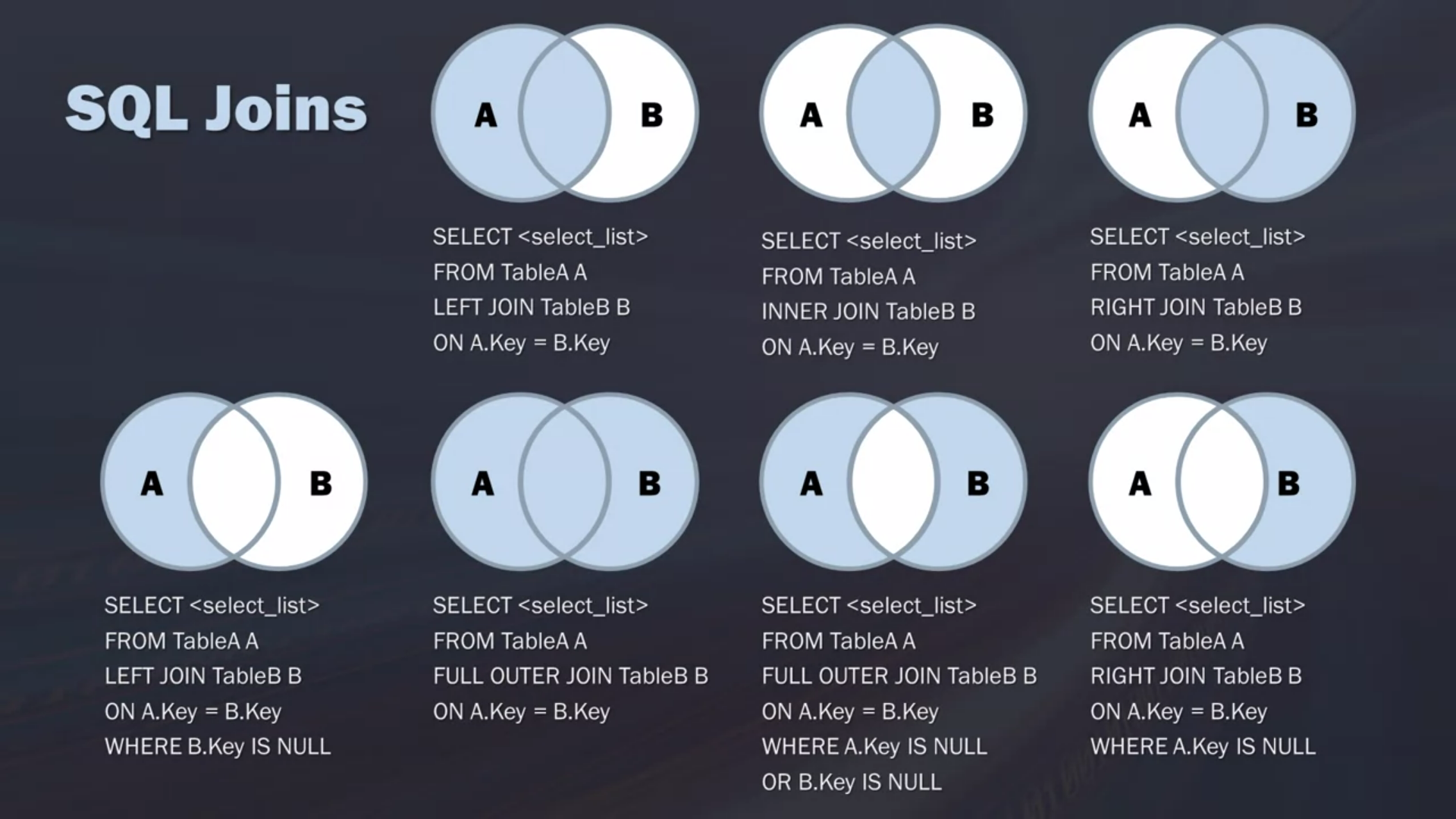
Left Join
Returns all records from the left table(tabe1), and the matched records from the right table(table2)
The result is NULL from the right side, if there is no match

I still want everything from the customer table.
I don't care if they didn't have an order but if they did, then bring it also all together and bring in one order table
Right Join
Returns all records from the right table(table2), and the matched records from the left table(table2)
The result is NULL from the left side when there is no match

Full Outer Join
Return all records when there is a match in either left(table1) or tight(talbe2) talbe records
"Give me everything"

Left Join
The following SQL statement will select all customers, and any orders they might have:

Right Join
The following SQL statement will return all employees, and any orders they might have placed:

- Difference between right and left is the order the tables are relating
- Left joins can be turned into right joins by reversing the order of the tables
Full Outer Join
Full Join / The following SQL statement selects all customers and all orders:
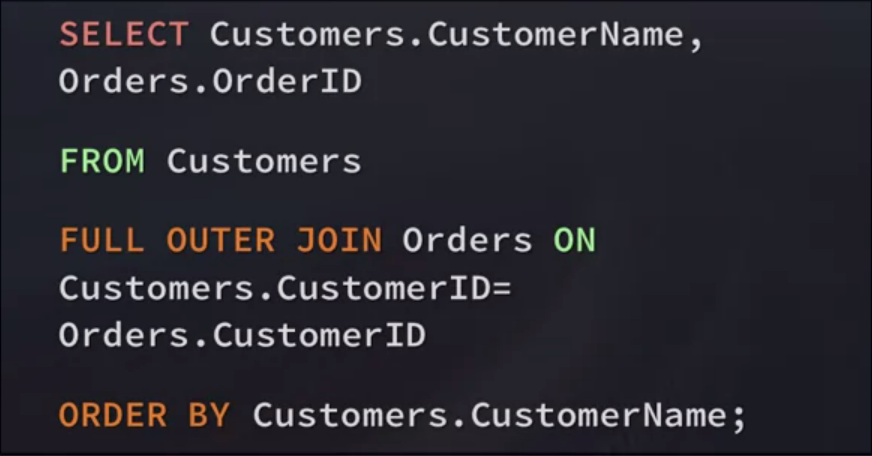
9. Unions
Learning Objectives
- Describe what a UNION is and how it works
- Discuss the rules for using UNIONs
- Write correct syntax for a UNION statement
- Describe a common situation in which UNIONS are useful
What is a Union?
- The UNION operator is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements
- Each SELECT statement within UNION must have the same number of columns
- Columns must have similar data types
- The columns in each SELECT statement must be in the same order
Union Example
Query 1: Basic Union Setup

Query 2: Which German cities have suppliers

SUMMARY
Best Practices Using Joins
It is easy to get results - you must make sure they are right results
Check the number of records
Does it seem logical given the kind of join you are performing?
Check for duplicates
Check the number of records each time you make a new join
Are you getting the results you expected?
Start small: one table at a time
"Slowly Do"
Think about what you are trying to do first
Map how you are joining data tables
Think about what your query is trying to do
Thinking first now will save time and frustration later
Joins and Database Performance
The more tables you join, the slower the database will perform
Don't grab unnecessary data if you don't need to
Be strategic
Take only what you need
Join Syntax
Always check the particular syntax for your DBMS
Remember SQLite does not do Right and FULL OUTER joins
SQL and Python
Python is a common language used for data science purposes. Many of you already know python or will soon be working in python. The following article goes over some of the differences in thinking between python and SQL.
Thinking in SQL vs Thinking in Python
Thinking in SQL vs Thinking in Python | Mode
Learn the difference between Python & SQL with our 6 tips. Understand & navigate these completely different frameworks for solving analytical problems.
mode.com
Union and Union All
In the video lectures in this module, we discussed the Union join. However, we didn’t go into detail regarding the differences between Union and Union all. Please read the following article for further explanation regarding the differences and performance of the two joins.
Difference Between Union and Union All - Optimal Performance Comparison
SQL SERVER - Difference Between Union vs. Union All - Optimal Performance Comparison - SQL Authority with Pinal Dave
More than a year ago I had written article SQL SERVER - Union vs. Union All - Which is better for performance? I have got many request to update this
blog.sqlauthority.com
'SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SQL] (2Week) Filtering, Sorting, and Calculating Data with SQL (0) | 2022.04.17 |
|---|---|
| [SQL] (1Week) Selecting and Retrieving Data with SQL (0) | 2022.04.13 |


